요청 매핑을 알아보자.

url을 가지고 매핑을 하였다.
// MappingController Class
package hello.springmvc.basic.requestmapping;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MappingController {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@RequestMapping("/hello-basic")
public String helloBasic() {
log.info("helloBasic");
return "ok";
}
}
Postman으로도 테스트를 해보자.
GET으로만 나오게 해 줄수 있다.
package hello.springmvc.basic.requestmapping;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MappingController {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello-basic", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloBasic() {
log.info("helloBasic");
return "ok";
}
}

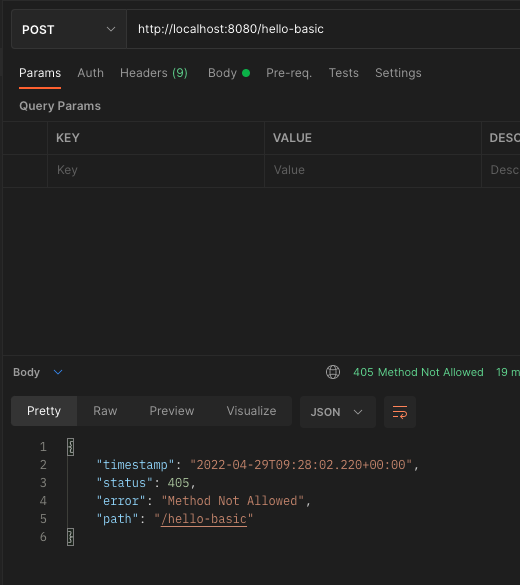
- 만약 여기에 POST 요청을 하면 스프링 MVC는 HTTP 405 상태코드(Method Not Allowed)를 반환한다.
HTTP 메서드 매핑을 축약 해줄수도 있다.
@GetMapping을 들어가보면 RequestMapping이 GET으로 되어있다.
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)@RestController
public class MappingController {
private Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@RequestMapping(value = "/hello-basic", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String helloBasic() {
log.info("helloBasic");
return "ok";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/mapping-get-v1", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String mappingGetV1() {
log.info("mappingGetV1");
return "ok";
}
/**
* 편리한 축약 애노테이션 (코드보기)
* @GetMapping
* @PostMapping
* @PutMapping
* @DeleteMapping
* @PatchMapping
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-get-v2")
public String mappingGetV2() {
log.info("mapping-get-v2");
return "ok";
}
}- HTTP 메서드를 축약한 애노테이션을 사용하는 것이 더 직관적이다. 코드를 보면 내부에서
- @RequestMapping 과 method 를 지정해서 사용하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
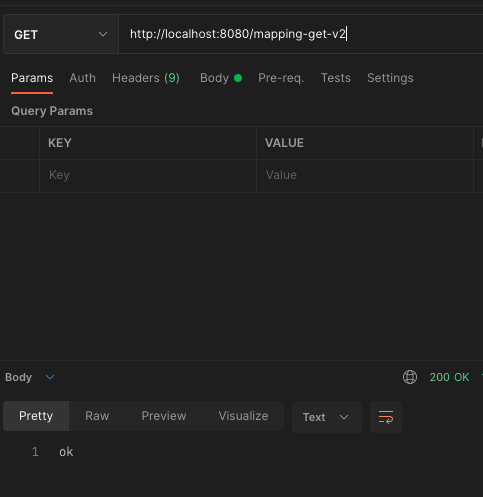
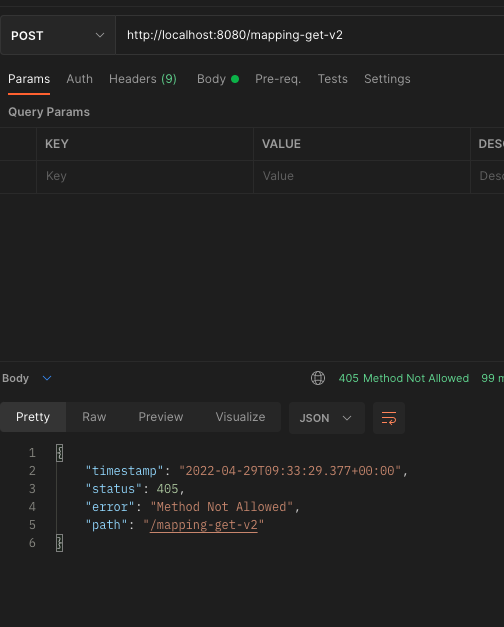
PathVariable도 한번 써보자. GetMapping에 있는 템플릿 형식의 값을 PathVariable로 꺼내서 쓸 수 있다.
/**
* PathVariable 사용
* 변수명이 같으면 생략 가능
* @PathVariable("userId") String userId -> @PathVariable userId
* URL 자체에 값이 들어가있다.
* /mapping/userA
*/
@GetMapping("/mapping/{userId}")
public String mappingPath(@PathVariable("userId") String data) {
log.info("mappingPath userId={}", data);
return "ok";
}

QueryParameter 방식과 비교
?userId = userA
PathVariable 방식
- /mapping/userA
- /users/1
- @RequestMapping 은 URL 경로를 템플릿화 할 수 있는데,
- @PathVariable 을 사용하면 매칭 되는 부분을편리하게 조회할 수 있다.
- @PathVariable 의 이름과 파라미터 이름이 같으면 생략할 수 있다.
PathVariable을 다중 사용할 수도 있다.
/**
* PathVariable 사용 다중
*/
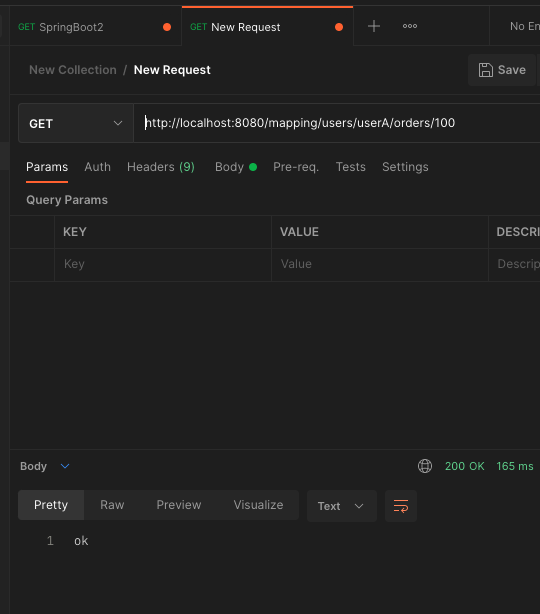
@GetMapping("/mapping/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}")
public String mappingPath(@PathVariable String userId, @PathVariable Long orderId) {
log.info("mappingPath userId={}, orderId={}", userId, orderId);
return "ok";
}
파라미터로 추가 매핑도 해보자.
// MappingController Class
/**
* 파라미터로 추가 매핑
* params="mode",
* params="!mode"
* params="mode=debug"
* params="mode!=debug" (! = )
* params = {"mode=debug","data=good"}
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-param", params = "mode=debug")
public String mappingParam() {
log.info("mappingParam");
return "ok";
}

파라미터가 없으면 매핑이 되지 않고 Postman에서 에러가 뜬다.
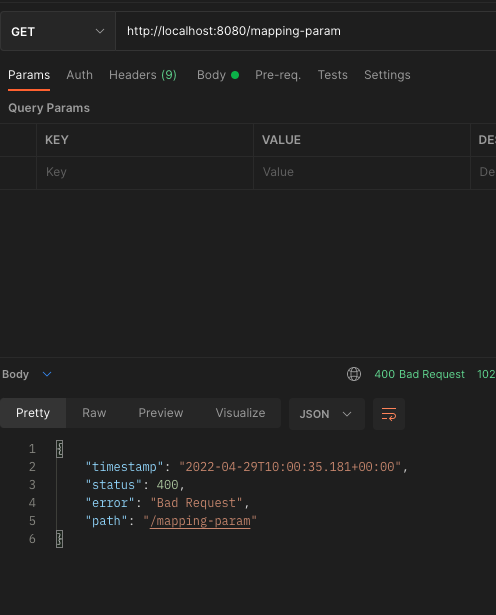
특정 헤더로 추가 매핑을 해보자.
header의 key value가 다 있어야 한다.
/**
* 특정 헤더로 추가 매핑
* headers="mode",
* headers="!mode"
* headers="mode=debug"
* headers="mode!=debug" (! = )
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/mapping-header", headers = "mode=debug")
public String mappingHeader() {
log.info("mappingHeader");
return "ok";
}
그리고 Content-Type 헤더 기반 추가 매핑을 해보자.
/**
* Content-Type 헤더 기반 추가 매핑 Media Type
* consumes="application/json"
* consumes="!application/json"
* consumes="application/*"
* consumes="*\/*"
* MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-consume", consumes = "application/json")
public String mappingConsumes() {
log.info("mappingConsumes");
return "ok";
}Body - raw에 JSON 형식으로 값을 입력하면

Headers에 Content-Type이 application/json으로 들어가게 된다.

POST로 해준다음 Send를 보내주게 되면 결과가 나온다.
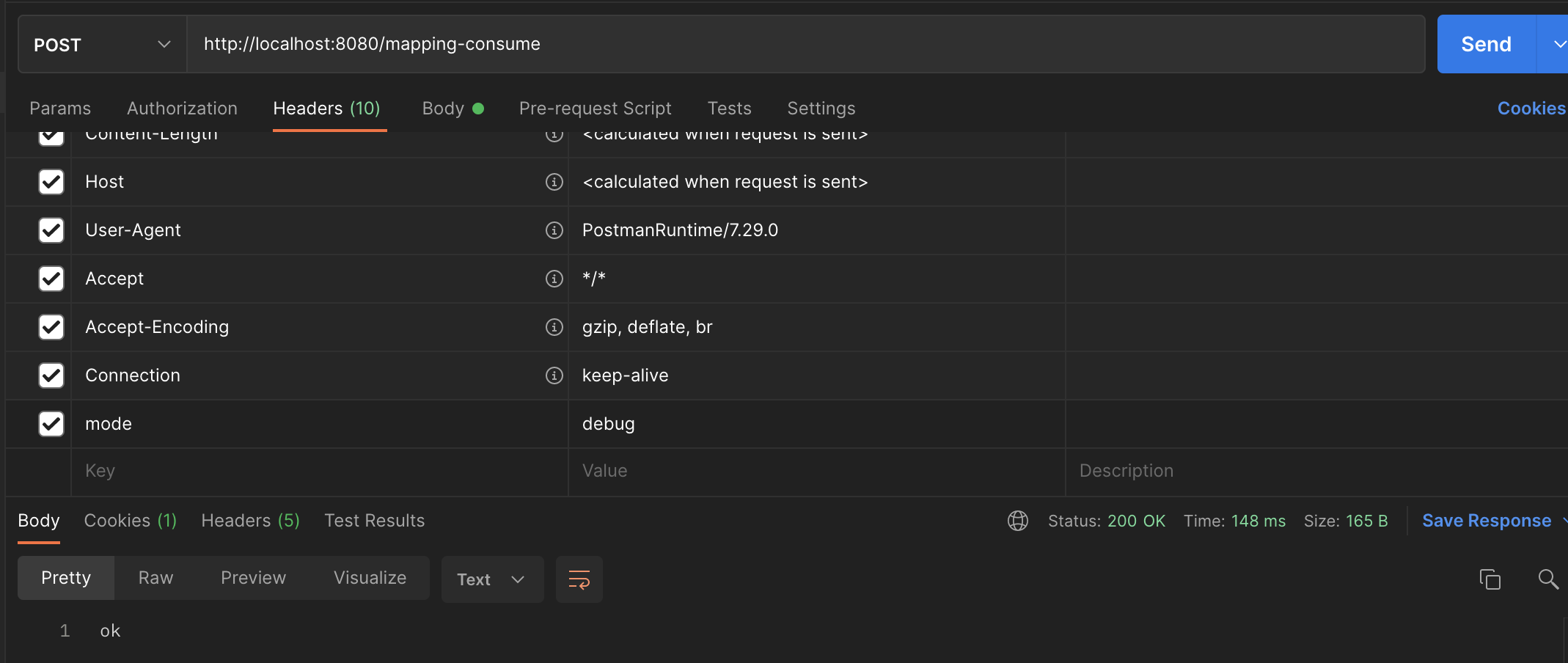
- Postman으로 테스트 해야 한다.
- HTTP 요청의 Content-Type 헤더를 기반으로 미디어 타입으로 매핑한다.
- 만약 맞지 않으면 HTTP 415 상태코드(Unsupported Media Type)을 반환한다.
미디어 타입 조건 매핑 - HTTP 요청 Accept, produce 관련해서 보면
Consume은 요청헤더의 Content-Type
produce는 요청헤더의 Accept
/*** Accept 헤더 기반 Media Type
* produces = "text/html"
* produces = "!text/html"
* produces = "text/*"
* produces = "*\/*"
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-produce", produces = "text/html")
public String mappingProduces() {
log.info("mappingProduces");
return "ok";
}
클라이언트가 Content-Type이 text.html인 것을 받아들일 수 있다. 라는 것이다.
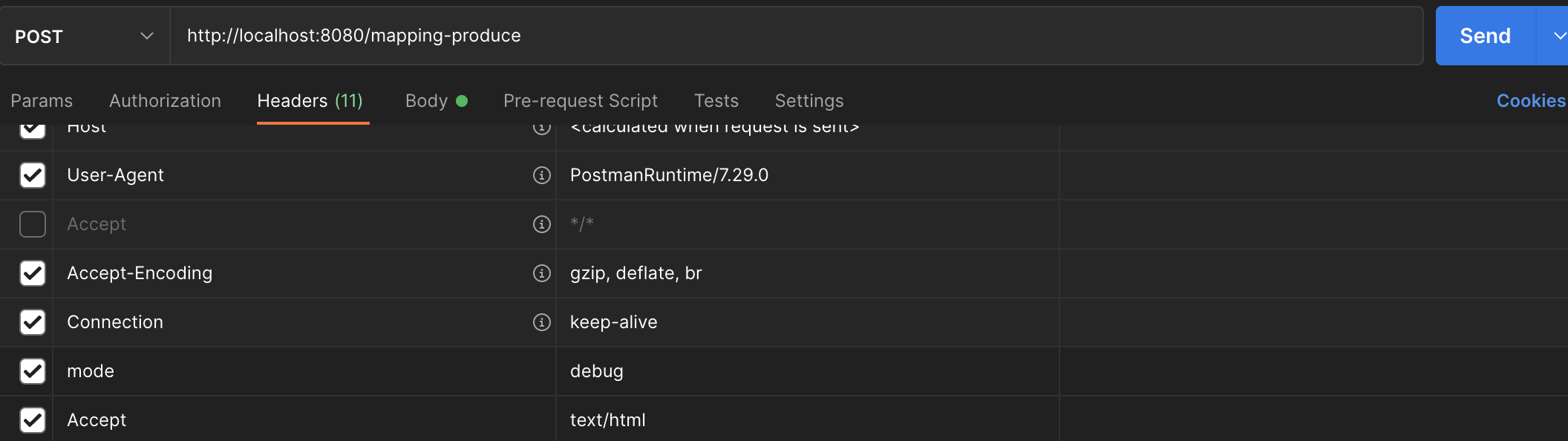

아래와 같이 consumes를 문자로 쓰는거 보다 MediaType으로 쓰는게 더 낫다.
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-consume", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
public String mappingConsumes() {
log.info("mappingConsumes");
return "ok";
}
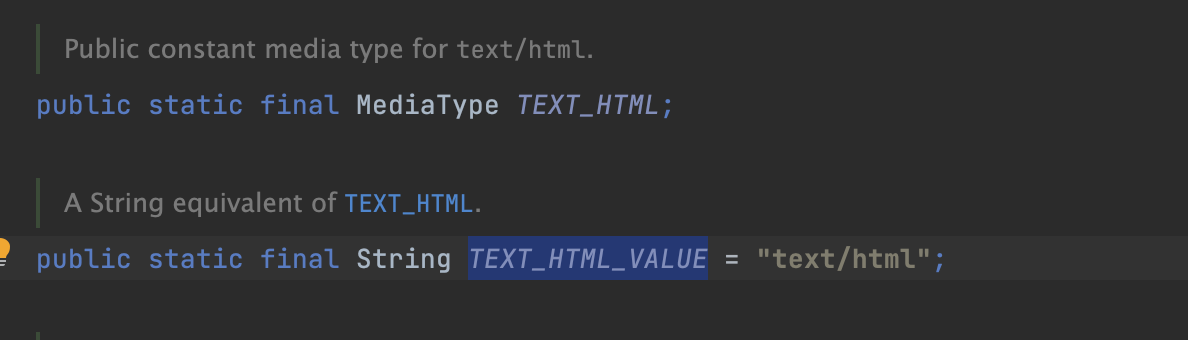
produces에서도 문자열 말고 TEXT_HTML_VALUE로 할 수 있다.
/*** Accept 헤더 기반 Media Type
* produces = "text/html"
* produces = "!text/html"
* produces = "text/*"
* produces = "*\/*"
*/
@PostMapping(value = "/mapping-produce", produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE)
public String mappingProduces() {
log.info("mappingProduces");
return "ok";
}
<출처 김영한: 스프링 MVC 1편 - 벡앤드 웹 개발 핵심 기술>
https://www.inflearn.com/course/%EC%8A%A4%ED%94%84%EB%A7%81-mvc-1/dashboard
스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술 - 인프런 | 강의
웹 애플리케이션을 개발할 때 필요한 모든 웹 기술을 기초부터 이해하고, 완성할 수 있습니다. 스프링 MVC의 핵심 원리와 구조를 이해하고, 더 깊이있는 백엔드 개발자로 성장할 수 있습니다., -
www.inflearn.com
'Spring > SpringMVC' 카테고리의 다른 글
| HTTP 요청 - 기본, 헤더 조회 (0) | 2022.04.29 |
|---|---|
| 요청 매핑 - API 예시 (0) | 2022.04.29 |
| 스프링MVC 기본기능 (0) | 2022.04.29 |
| SpringMVC 구조 정리 (0) | 2022.04.28 |
| 스프링 MVC를 시작과 컨트롤러 통합 & 실용적인 방식 (0) | 2022.04.28 |